

It is often not calculated as a fraction of the extracellular fluid, but it is about 2.5% of the total body water It is the smallest component of extracellular fluid, which also includes interstitial fluid and plasma. Transcellular fluid is the portion of total body water contained within the epithelial-lined spaces. The main function of the transcellular fluid is to lubricate the body cavities and provide nutrients A body fluid that is not inside cells but is separated from plasma and interstitial fluid by cellular barriers The transcellular fluid includes the cerebrospinal fluid, joint fluid, ocular fluid, and pleural fluid. Transcellular fluid is the total body water found within the epithelial-lined spaces. About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features © 2020. Transcellular fluid meaning - transcellular fluid d. Transcellular fluid is the portion of total body water contained within epithelial -lined spaces One classic example is the movement of glucose from the intestinal lumen to extracellular fluid by epithelial cells Interstitial fluid (or tissue fluid) is a solution that bathes and surrounds the cells of multicellular animals. Transcellular transport involves the transportation of solutes by a cell through a cell. For the complementary transport route, see Paracellular transport.
#BODY FLUID COMPARTMENTS TRANSCELLULAR FREE#
It is important because of the specialised functions involved From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. It includes CSF, GIT fluids, bladder urine, aqueous humour and joint fluid. It is contained within epithelial lined spaces. Transcellular fluid is a small compartment that represents all those body fluids which are formed from the transport activities of cells. Chloride enters enterocytes at the basolateral membrane via the electroneutral Na + /K + /2Cl − cotransporter (gene NKCC1, SLC12A2) and then Cl − exits the enterocyte via chloride channels in the apical membrane Examples of this fluid are cerebrospinal fluid, ocular fluid and joint fluid Transcellular secretion of chloride is the main process leading to fluid secretion in the normal small intestine. It is often not calculated as a fraction of the extracellular fluid, but it is about 2.5% of the total body water or 5% of extracellular fluid. Transcellular fluid is the portion of total body water contained within epithelial lined spaces. Transcellular fluids include cerebrospinal, pericardial, pleural, peritoneal, synovial, and intraocular fluids and sweat and. Fluid and Electrolyte Management Across the Age Continuum. It is the intravascular fluid part of extracellular fluid (all body fluid outside of cells) Transcellular fluids are also a component of ECF and are found in the cerebrospinal column, pleural cavity, lymph system, joints, glandular secretions, and eyes.

The extracellular fluid also includes the transcellular fluid making up only about 2.5% of the ECF. The intracellular fluid of the cytosol or intracellular fluid (or cytoplasm) is the fluid found inside cells. This compartment is characterized by being formed from the secretions of epithelial cells This fluid is not in contact with the interstitial compartment- rather, it is I contact with the cells. This is a small but important compartment 2.5% of total body fluid is locked up in these secretions.

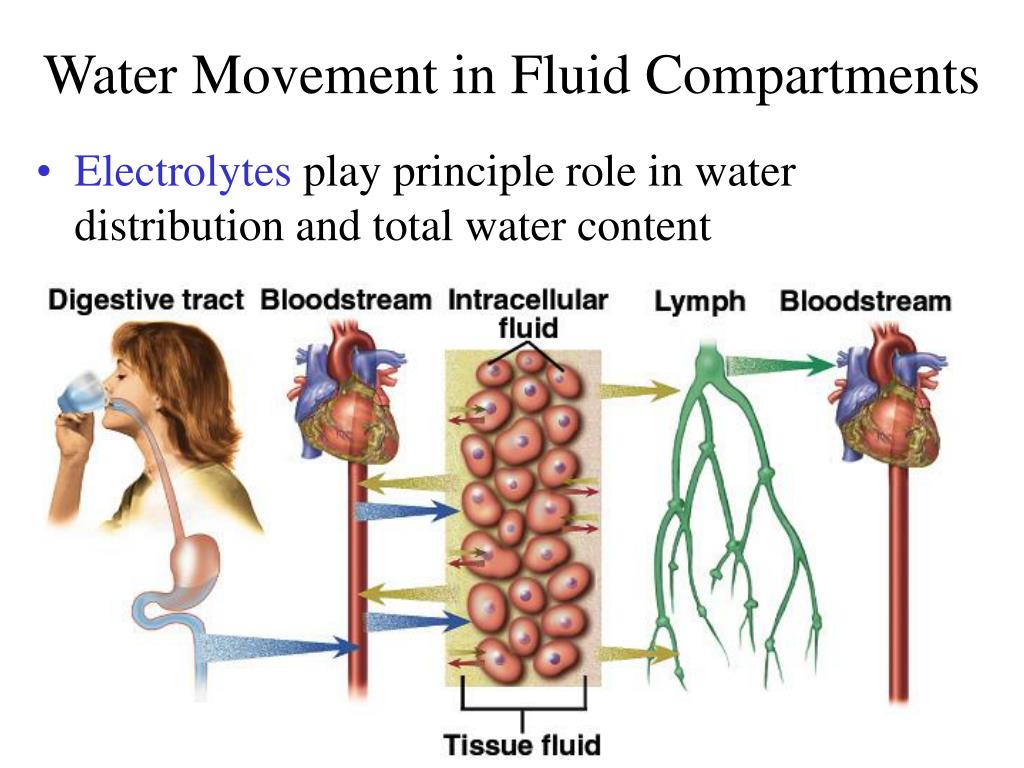
ids the fluids that are not inside cells, but are separated from plasma and interstitial fluid by cellular barriers for example, cerebrospinal fluid, synovial fluid, pleural fluid Transcellular fluid.The ECF should be viewed as a physiological rather than a strictly definable. Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Balance. Fluids in the body are distributed in two compartments: the intracellular. Transcellular Fluid Fluids, Electrolytes, and Acid-Base Therapy.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
